 In an entirely new approach to treating asthma and allergies, a biodegradable nanoparticle acts like a Trojan horse, hiding an allergen in a friendly shell, to convince the immune system not to attack it, according to new Northwestern Medicine research. As a result, the allergic reaction in the airways is shut down long- term and an asthma attack prevented.
In an entirely new approach to treating asthma and allergies, a biodegradable nanoparticle acts like a Trojan horse, hiding an allergen in a friendly shell, to convince the immune system not to attack it, according to new Northwestern Medicine research. As a result, the allergic reaction in the airways is shut down long- term and an asthma attack prevented.
The technology can be applied to food allergies as well. The nanoparticle is currently being tested in a mouse model of peanut allergy, similar to food allergy in humans.
“The findings represent a novel, safe and effective long-term way to treat and potentially ‘cure’ patients with life-threatening respiratory and food allergies,” said senior author Stephen Miller, the Judy Gugenheim Research Professor of Microbiology-Immunology at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine. “This may eliminate the need for life-long use of medications to treat lung allergy.”
It’s the first time this method for creating tolerance in the immune system has been used in allergic diseases. The approach has been used in autoimmune diseases including multiple sclerosis and celiac disease in previous preclinical Northwestern research.
The asthma allergy study was in mice, but the technology is progressing to clinical trials in autoimmune disease. The nanoparticle technology is being developed commercially by Cour Pharmaceuticals Development Co., which is working with Miller to bring this new approach to patients. A clinical trial using the nanoparticles to treat celiac disease is in development.
The paper will be published April 18 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
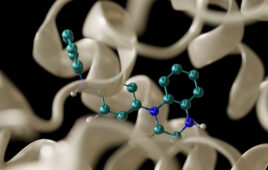
“It’s a universal treatment,” Miller said. “Depending on what allergy you want to eliminate, you can load up the nanoparticle with ragweed pollen or a peanut protein.”
The nanoparticles are composed of an FDA-approved biopolymer called PLGA that includes lactic acid and glycolic acid.
Also a senior author is Lonnie Shea, adjunct professor of chemical and biological engineering at Northwestern’s McCormick School of Engineering and of obstetrics and gynecology at Feinberg, and chair of biomedical engineering at the University of Michigan.
When the allergen-loaded nanoparticle is injected into the bloodstream of mice, the immune system isn’t concerned with it because it sees the particle as innocuous debris. Then the nanoparticle and its hidden cargo are consumed by a macrophage, essentially a vacuum-cleaner cell.
“The vacuum-cleaner cell presents the allergen or antigen to the immune system in a way that says, ‘No worries, this belongs here,'” Miller said. The immune system then shuts down its attack on the allergen, and the immune system is reset to normal.
The allergen, in this case egg protein, was administered into the lungs of mice who have been pretreated to be allergic to the protein and already had antibodies in their blood against it. So when they were re-exposed to it, they responded with an allergic response like asthma. After being treated with the nanoparticle, they no longer had an allergic response to the allergen.
The approach also has a second benefit. It creates a more normal, balanced immune system by increasing the number of regulatory T cells, immune cells important for recognizing the airway allergens as normal. This method turns off the dangerous Th2 T cell that causes the allergy and expands the good, calming regulatory T cells.
Filed Under: Genomics/Proteomics