 Data from Janssen’s phase 3b COSMOS clinical trial reveals that guselkumab (Tremfya), an inhibitor of interleukin-23 (IL-23), provides improvements in all minimal disease activity (MDA) domains for adults with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA). The benefits persist through week 48, even in patients who have seen inadequate responses to one or two tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi-IR).
Data from Janssen’s phase 3b COSMOS clinical trial reveals that guselkumab (Tremfya), an inhibitor of interleukin-23 (IL-23), provides improvements in all minimal disease activity (MDA) domains for adults with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA). The benefits persist through week 48, even in patients who have seen inadequate responses to one or two tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi-IR).
The drug also had an acceptable safety profile in the study. These results are among 41 Janssen-backed abstracts being presented at the 2023 Annual European Congress of Rheumatology (EULAR) meeting scheduled for May 31 to June 3, 2023 in Milan.
In a separate post-hoc analysis of the phase 3 DISCOVER-1 and DISCOVER-2 studies, guselkumab demonstrated swift and long-lasting durability in all evaluated criteria, including dimensions related to patient-reported pain, physical components of health-related quality of life and fatigue.
Efficacy of guselkumab: A post-hoc analysis of phase 3 DISCOVER studies
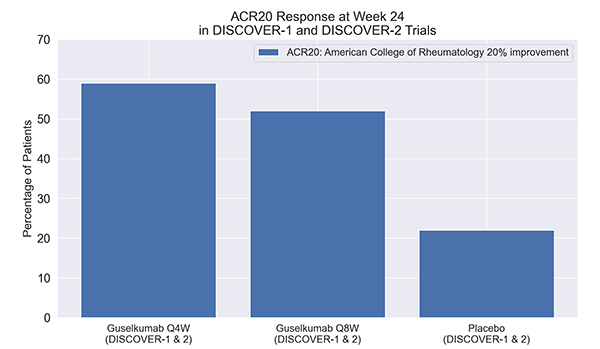
Percentage of patients achieving ACR20 with TREMFYA at Weeks 4 and 8: A Post-Hoc Analysis of Phase 3 DISCOVER Studies. Developed by the American College of Rheumatology, ACR20 is a clinical metric indicating a 20% improvement in specified symptoms or measures in rheumatic disease trials.
The data continues to strengthen the case that IL-23 drugs offer sustained effectiveness in psoriatic arthritis, a chronic, progressive disease involving painful joints and skin inflammation. Up to 1% of the world’s population has the condition, according to an epidemiological review published in Best Practice & Research Clinical Rheumatology.
Other IL-23 inhibitors include risankizumab-rzaa (Skyrizi) and tildrakizumab-asmn (Ilumya). Risankizumab has won FDA approval for plaque psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis and Crohn’s disease. Tildrakizumab-asmn (Ilumya) is currently indicated only for the treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in adults who are candidates for systemic therapy or phototherapy.
Outside of IL-23 inhibitors, drug companies offer several treatments for psoriatic arthritis, including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), biologics and TNF inhibitors. Examples of TNF inhibitors include therapies such as etanercept, adalimumab, golimumab or certolizumab pegol. Many patients, however, have an inadequate response to these treatments. A 2022 paper in Clinical Rheumatology noted that 77% of patients with psoriatic arthritis did not respond well to the advanced therapies within a year of starting treatment.
Guselkumab fared well in a network meta-analysis last year
A network meta-analysis published last year ranked guselkumab best for skin clearance in psoriatic arthritis.
Guselkumab, developed by Janssen, has scored a handful of regulatory wins since it was first submitted to the FDA in November 2016 for the treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. It has received multiple approvals including for a One-Press patient-controlled injector in February 2019, and as the first selective IL-23 inhibitor for active psoriatic arthritis in July 2020. In 2022, it generated $2.7 billion in revenue, clocking in at the 41st best-selling drug of that year.

Predictors of achievement of patient-reported Minimal Disease Activity (MDA) domains at Week 48 in patients with Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA) inadequately responding to TNF inhibitors, treated with guselkumab in the COSMOS study. The table outlines different baseline variables (BL variables) and how they influenced different MDA parameters, including HAQ-DI (Health Assessment Questionnaire – Disability Index) ≤0.5, Patient pain ≤15, Methotrexate (MTX) Use, Patient Global Assessment (PtGA) ≤20, Tender Joint Count (TJC) ≤1 and the FACIT fatigue score, a scale is a questionnaire used to assess levels of fatigue in patients. The predictors are reported as odds ratios, hazard ratios, or simple measures with 95% confidence intervals.
A post-hoc analysis of the Phase 3b COSMOS clinical trial showed that guselkumab provided sustained improvement in all MDA domains from baseline through week 48 in adult patients living with active PsA and who were inadequate responders to one to two TNFis (n=189).
The COSMOS study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of guselkumab in comparison with a placebo in participants with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA) who had an inadequate response to Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha (TNF-alpha) therapy.
The study comprised two parts: a 24-week double-blind, placebo-controlled period for the primary analysis of the efficacy and safety of guselkumab versus placebo, and a 32-week active-treatment and safety follow-up period for additional analysis of the efficacy and safety of guselkumab. The trial monitored the safety of the participants throughout the study period spanning up to week 56.
Some 285 participants enrolled in the study, which adopted a parallel assignment intervention model, and employed triple masking (participant, investigator, outcomes assessor) to ensure unbiased results.
While further studies are needed to confirm these findings and to explore more about the long-term safety and efficacy of guselkumab, the COSMOS and DISCOVER studies offer hope for psoriatic arthritis patients searching for more effective treatment options.
Filed Under: Biologics, clinical trials, Drug Discovery, Rheumatology





Tell Us What You Think!
You must be logged in to post a comment.