Blood Thinner Found to Significantly Reduce Subsequent Heart Failure Risks
In Mice, Eliminating Damaged Mitochondria Alleviates Chronic Inflammatory Disease
Inflammation is a balanced physiological response — the body needs it to eliminate invasive organisms and foreign irritants, but excessive inflammation can harm healthy cells, contributing to aging and chronic diseases. To help keep tabs on inflammation, immune cells employ a molecular machine called the NLRP3 inflammasome. NLRP3 is inactive in a healthy cell, but…
An Errant Editing Enzyme Promotes Tumor Suppressor Loss and Leukemia Propagation
Writing in the January 3 issue of Cancer Cell, researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine report that detection of “copy editing” by a stem cell enzyme called ADAR1, which is active in more than 20 tumor types, may provide a kind of molecular radar for early detection of malignancies and represent…
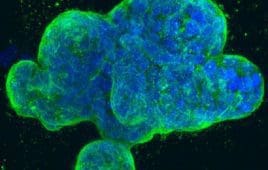
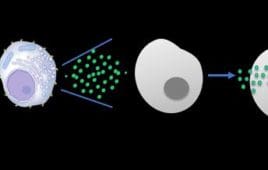
New Cancer Immunotherapy Approach Turns Human Cells into Tiny Anti-Tumor Drug Factories
Cancer immunotherapy — efforts to better arm a patient’s own immune system to attack tumors — has shown great potential for treating some cancers. Yet immunotherapy doesn’t work for everyone, and some types of treatment can cause serious side effects. In a new approach, researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine are…
Immunotherapy Better Than Chemotherapy for Subtype of Head, Neck Cancer
Is the Next Big Step in Cancer Therapy Personalized Vaccines?
Researchers Evaluate Controversial Treatment for Parkinson’s Disease Psychosis
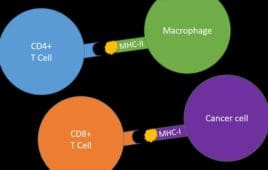
Cancer Immunotherapy Might Benefit From Previously Overlooked Immune Players
Cancer immunotherapy — efforts to boost a patient’s own immune system, allowing it to better fight cancer cells on its own — has shown great promise for some previously intractable cancers. Yet immunotherapy doesn’t work for everyone, for reasons that aren’t always clear. Most research and new therapies in this field have been focused on…
Cancer Drug and Antidepressants Provide Clues for Treating Brain-Eating Amoeba Infections
The amoeba Naegleria fowleri is commonly found in warm swimming pools, lakes and rivers. On rare occasions, the amoeba can infect a healthy person and cause severe primary amebic meningoencephalitis, a “brain-eating” disease that is almost always fatal. Other than trial-and-error with general antifungal medications, there are no treatments for the infection. Researchers at Skaggs School of…
CAR-T Immunotherapies May Have a New Player
Emerging CAR-T immunotherapies leverage modified versions of patient’s T-cells to target and kill cancer cells. In a new study, published June 28 online in Cell Stem Cell, researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine and University of Minnesota report that similarly modified natural killer (NK) cells derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells…
Stem Cell-Based Phase I Trial to Repair Spinal Cord Injuries Produces Encouraging Results
Repurposed Drug Found to be Effective Against Zika Virus
In both cell cultures and mouse models, a drug used to treat Hepatitis C effectively protected and rescued neural cells infected by the Zika virus — and blocked transmission of the virus to mouse fetuses. Writing in the current online issue of the journal Scientific Reports, researchers at University of California San Diego School of…
Experimental Drug Blocks Toxic Ion Flow Linked To Alzheimer’s Disease
An international team of researchers has shown that a new small-molecule drug can restore brain function and memory in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. The drug works by stopping toxic ion flow in the brain that is known to trigger nerve cell death. Scientists envision that this drug could be used to treat Alzheimer’s…
Antibiotics Effective Against Drug-Resistant Bacteria in Pediatric Skin Infections
Antibiotic effective against drug-resistant bacteria in pediatric skin infections. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a bacterial scourge. As its name suggests, MRSA is resistant to most common antibiotics and thus difficult to treat, particularly in children where it commonly causes complicated skin and skin structure infections. In a randomized, controlled clinical trial — the first of its…
Potential New Drug Class Hits Multiple Cancer Cell Targets
Drug Leads Identified to Combat Heart Disease
Using a unique computational approach to rapidly sample, in millisecond time intervals, proteins in their natural state of gyrating, bobbing, and weaving, a research team from UC San Diego and Monash University in Australia has identified promising drug leads that may selectively combat heart disease, from arrhythmias to cardiac failure. Reported in the September 5,…